Calculation of a ribbon foundation under the house Useful advice,Construction,Building materials

The construction of the house begins with the construction of the foundation. The strength and durability of the built on it at home will depend on the quality of the foundation. The cost of this lower part of the future build is about a quarter of the total cost of the house. In addition, this time-consuming process and requires a clear understanding of its ultimate goal. Errors made in the calculations and when the foundation is erected, when they are corrected, very expensive. Often the amounts on the alteration of marriage even exceed the initial costs. Avoid mistakes in the construction of the foundation, you can only competently with its calculation and execution.
Content
- Description of the tape foundation under the house
- Terms, definitions and parameters for calculating the tape foundation under the house
- The procedure for calculating the tape foundation under the house
- Determination of the depth of the bunch of tape foundation
- Calculation of the soles of the foundation
- Calculation of the soles of the base of the base of the bearing capacity
- Calculation of the sole size of the foundation based on admissible design deformations
- Calculation of the height of the socle
- Calculation of the number of materials and the total value of the belt foundation
- Video on the topic
Description of the tape foundation under the house
Ribbon foundation is universal. This type of foundation is suitable for houses with any design of the walls.
In cross section, the ribbon foundation of the house forms a rectangle located vertically. The upper part of this rectangle should take into account the slope of the construction site and act as a concentration of about 100 mm above the plane of the adjacent ground surface. In addition, the upper edge of the foundation, depending on the design of the walls of the house, can be wider than the wall thickness.
When building a residential building in 1-3 floors, the transverse dimensions of the belt foundation are usually not very different. This can be explained by the fact that the load from the house on the ground is insignificant, while the area of \u200b\u200bthe basement of the foundation will always be more necessary for the calculation of approximately 2-3 times.
Thus, depending on the material used in the creation of a belt basement, the average width for bob foundations is 600 mm; for concrete or reinforced concrete and boot concrete 400-600 mm; For foundations made of bricks are 500-550 mm. Such a width of the base of the belt foundation provides a dressing of vertical seams of stones and is convenient to work, reducing extra labor.
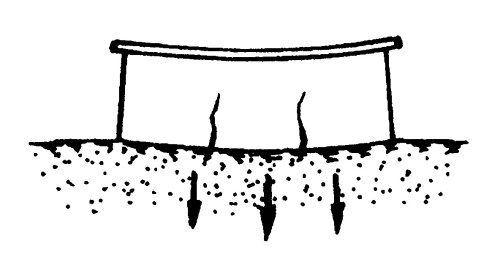
If the ground on the construction site is weak or inhomogeneous, then most likely, the pressure of the house with its weight on such a soil will exceed the normative (for the middle of Russia, it is 1-1.5 kg / cm²). In this case, it is necessary to increase the width of the base of the foundation. This can be created by the creation of ledges in the foundation height every 300-600 mm. In addition, it is possible at the bottom of the foundation to create a "pillow", placing the reinforced concrete slab or the tumper of a large sample sand, with grain grains with a size of 1-2 mm, with a layer of 200-300 mm thick.
Terms, definitions and parameters for calculating the tape foundation under the house
Foundation - The lower part of the house underground, intended for transmitting and distributing the load from the building to the ground.
Sole of the foundation - The foundation plane is directly interacting with the soil.
Depth of the Boundage of Foundation - distance from the sole of the foundation to the surface of the soil.
The underlying layer of soil (base) - The ground layer, on which the foundation sole is based on.
The calculated depth of the primer of the soil- The position of the freezing boundary relative to the soil level adopted as the calculated value (SNiP standards).
Ground water level - The position of groundwater mirrors relative to the ground level in the conditionally open pit (well).
Compressible ground thickness - The deformable part of the soil, perceiving the load from the foundation.
The procedure for calculating the tape foundation under the house
Determination of the depth of the bunch of tape foundation
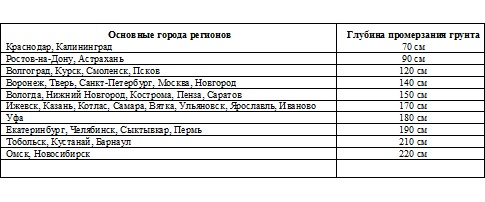
The depth of the foundation depends on the depth of the freezing of soils, the level of groundwater and from the underlying layer of the soil. Typically, the depth of the foundation is chosen below the drainage depth, but not less than 500 mm.
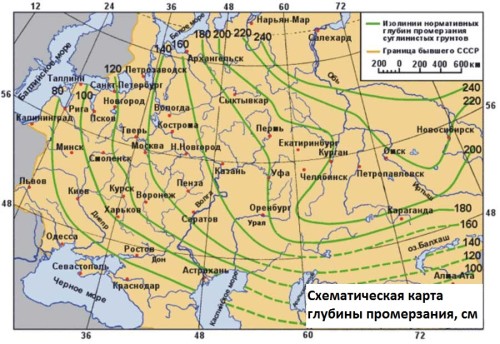
The drainage depth is determined by the climatic conditions of the region and corresponds to the greatest value of the freezing of the wet soil without snow cover at the lowest fixed temperatures. It can be determined from the table:
In addition, it must be borne in mind that with year-round accommodation in the house, when it warms it in winter due to heating, the calculated depth of the primer of the soil decreases by 15-20%.
Also, the estimated depth of the primer of the soil can be determined by the formula:
d.f \u003d.k.n × d.fn,
where:
k.n -the coefficient that takes into account the influence of the thermal regime of the structure is accepted according to Table 1 SNiP 2.02.01-83 bases and foundations;
d.fn -the regulatory depth of the seasonal freezing of the soil is taken on the climatic map "Zoning the territory of the Russian Federation by the mass of snow cover."
When calculating the depth of the foundation of the basement relative to groundwater, tend to ensure that the basement of the foundation passes the load on the durable layer of soil. Such a layer is located above the level of groundwater, which depends on the geological conditions of the locality, where the construction site is located.
When calculating the depth of the foundation, taking into account the presence of the design features of the house, the depth of the basement is also taken into account.
Thus, the depth of the foundation is equal to the maximum value consisting of values \u200b\u200bcalculated from climatic (the depth of the primer of the soil), the geological (depth of groundwater) and the structural (presence of the basement) of features.
Calculation of the soles of the foundation
The definition of geometric parameters, the main of which is the area of \u200b\u200bthe basement sole, also the responsible stage of the calculation. Since the reliability of further operation of the house depends on the correctness of its definition. If the support area is less necessary, it will entail an uneven decor of the structure and its deformation. The excess area of \u200b\u200bthe basement soles is unjustified additional costs.
There are two options for calculating the area of \u200b\u200bthe basement of the foundation for limit states. The first option for calculating the bearing ability of the base, the second for admissible design deformations.
Calculation of the soles of the base of the base of the bearing capacity of the base
It consists in assessing the stability of the underlying soil layer to the effects of the weight of the structure. Under the influence of operational loads due to the seal of the soil base, a deformation shift of the soil layers occurs and the foundation is arisen. The depth of the precipitate depends on both the strength of the ground-base and the amount of the pressure of the force. For calculation, there is a formula:
S\u003e υn.F / υ.c.R.o ,
where:
S. - the area of \u200b\u200bthe basement soles (see 2);
F. - settlement load on the base (total weight of the house with an additional operational load) (kg);
ϒn. — reliability coefficient (equal to 1,2);
ϒ c. — coefficient of working conditions;
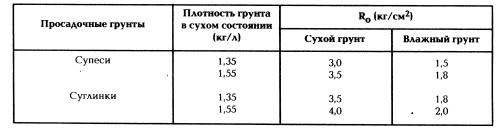
R.the conditioned calculated resistance of the ground ground for the foundation.
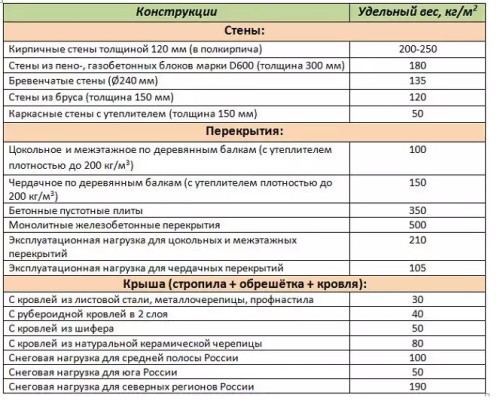
The total weight of the house with an additional operational load is the amount of values:
- mass of the walls of the house with frontones and with internal partitions;
- the mass of the base and inter-storey floors;
- the weight of the roof taking into account the material of the roof and snow load.
There are convenient online calculators to calculate the weight burden on the foundation that can be used. For approximate calculation of the total weight of the house, you can use the table:
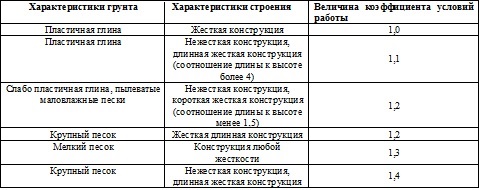
The coefficient of working conditions is values:
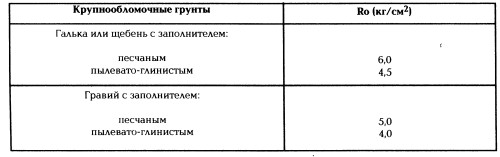
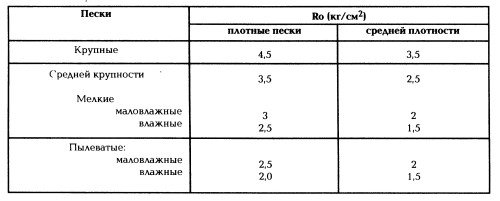
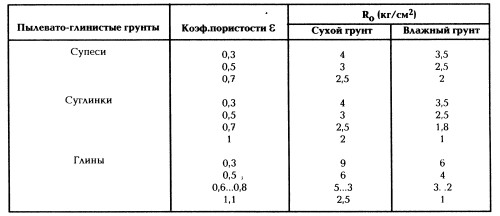
The conditional calculation resistance of the ground ground for the foundation is determined by the tables:
Calculation of the sole size of the foundation based on admissible design deformations
In contrast to the first option for calculating the area of \u200b\u200bthe foundation, this option makes it possible to exclude the deformation of the structure of the house from the uneven drawdown of the foundation. This is ensured by the assessment of the compliance of the real and permissible level of deformation of the structure from the impact of operational loads.
There are the following types of deformations of the construction of structures:
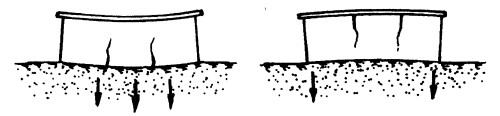
Dogibe and Fig- It occurs due to the uneven precipitation of the foundation.
Shift -it occurs when the foundation is sediment with one of the parties.
Roll -it occurs at high flexural stiffness of the structure (high-rise design or element).
Skew - It occurs when the foundation is uneven sediment on one of the plots.
Horizontal displacement - It occurs in the foundations, in the walls of basements, in retaining walls in areas loaded with horizontal efforts.
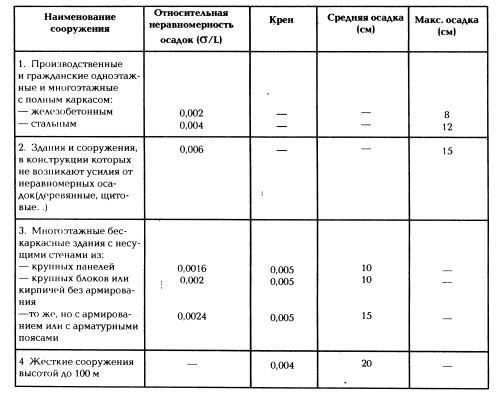
The permissible values \u200b\u200bof the deformations of structures depend on the characteristics of the design and used in the construction of materials are shown in the table:
Relative unevenness of precipitation — The maximum ratio of the difference in the sediment of two areas of the foundation to the distance between them. Based on this value, it is possible to determine the minimum range of distances between the areas with the unevenness of the precipitate, and determine the calculated area of \u200b\u200bthe foundation.
Example:
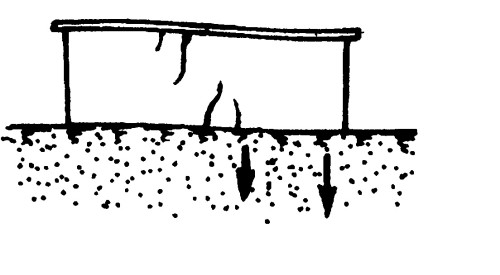
Suppose that a two-storey brick house was deformed in the form of a deflection in the center of 1 cm.
The distance along the length of the foundation between the measurement points of the deflection site is 600 cm. With the length of the structure of 12 m, the relative unevenness of the precipitate is 1/600 \u003d 0.0017. The permissible unevenness of the sediment of such a structure is 0.002. Consequently, the sediment is 1 cm is acceptable.
Calculation of the height of the socle
The height of the base is calculated taking into account the climatic characteristics of the area of \u200b\u200bthe construction site in the magnitude of the snow cover and the necessary characteristics of the stiffness of the cross section of the foundation.
Calculation of the number of materials and the total value of the belt foundation
Calculation of reinforcement for a belt foundation
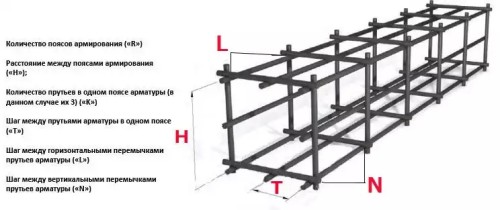
Reinforcement of the belt foundation is necessary to increase the resilience of deformations and operational loads of the structure. For the reinforcement of the foundation, you will need to calculate the diameter and the number of reinforcement rods.
From the practice and technical documentation it follows that the number of reinforcement must be at least 0.1% of the area of \u200b\u200bthe base cross section.
Calculation of the diameter of the reinforcement:
- For light designs - 8 mm.
- For medium structures - 10-12 mm.
- For heavy buildings - 14 mm.
Calculation of the number of reinforcement rods:
- To calculate the general element of horizontal rods, it is necessary to multiply the perimeter of the entire foundation to 4.
- To calculate the number of jumpers, it is necessary to divide the total length of the foundation to the planned length between the jumpers and also multiply by 4.
- If the foundation is illuminated and provides for two frames, then when calculating all the results are simply doubled.
- When calculating the number of rods, it is possible to proceed from the standard length of reinforcement rods - 6 m.
Example:
For a belt foundation for a house 6× 8 m with two partitions 6 m and 4 m has a perimeter (6 + 8) × 2 \u003d 28 m. Taking into account partitions, the total perimeter will be 28 + 6 + 4 \u003d 38 meters. So the total fittings will be 38 × 4 \u003d 152 m. Taking into account the length of the reinforcement rod - 6 m on the 8 m site will take another 2 m of the rod for which the remains of the 4-meter partition are suitable. Thus, it turns out (4 + 4)nS 2 \u003d 8 junctions. Taking into account the adhesion of the rods at the joints of 0.5 m in both sides, it will take 152 + 8 \u003d 160 m of reinforcement. In pieces it will be 160/6 \u003d 26.6, round up to 27 pieces of the reinforcement rod. For jumpers with a distance of viscosion 0.5 m, with the length of the foundation 38 m, for vertical and horizontal rods will be needed 38 / 0.5 × 4 \u003d 304 pieces. With a frame height of 0.5 m and a width of 0.25 m on the horizon will go 304/2 × 0.25 \u003d 38 m, and vertical 304/2 × 0.5 \u003d 76 m reinforcing rod. The number of rods on the jumper is obtained (38 + 76) / 6 \u003d 19 pieces.
Calculation of concrete on a ribbon foundation
To calculate the number of concrete on the construction of a belt foundation, there is a simple formula:
TObς \u003d. NSf × Vf × ( D.1+D.2),
where
TObς - the required amount of concrete;
NSf - the width of the foundation;
Vf - the height of the foundation;
D.1 - length of the inside of the structure;
D.2 — The length of the exterior of the design.
Calculation of the value of the ribbon foundation
To calculate the cost of a belt foundation, it is necessary to clarify the current prices for the materials used and multiplied by the values \u200b\u200bobtained during the calculations described above.
Most more concrete will cost. Its cost will be 25% of all costs for the foundation. Then from 15% to 20% of expenses, depending on sizes and quality, will go to fittings. Formwork will require 10% of the total cost. Next, 5% of the cost is transportation costs. Others, not the smallest 40-45% of expenses will require sand, wire for mating, waterproofing material, brick, fasteners, tools, etc.
There are also convenient online calculators for the complete calculation of the belt foundation and video with detailed instructions.