
Epoxy Resin, Application and Properties Building materials

Calio "Epoxy" is familiar with almost every person of conscious age. Epoxy resin is a variety of synthetic resins. She appeared in the fifties and immediately gained great popularity thanks to universal consumer properties.
Content
- What is epoxy resin
- What is hardener
- What should be the ratio of resin and hardener
- From what depends the curing rate of epoxy resin
- Advantages of epoxy resin
- Types of epoxy resin
- Where epoxy resin is used
- Preparation of the surface for applying epoxy resin
- Epoxy adhesive
- How to prepare a large volume of epoxy resin
- What is "lifetime" epoxy resin
- How to make bulk products from epoxy resin
- How to give an epoxy resin color
- With which you can combine epoxy resin
- Safety rules
- Characteristics Epoxy Resin ED-20
- Epoxy Resin Quality Standards
- Use epoxy resin for protective wood coating
- Application of Epoxy Resin for Fiberglass Suit
- Strength for century
Epoxy resins are widely used in the household, and in industrial production. The possibilities of using epoxy resins are constantly expanding due to the development of new compositions with improved characteristics.
What is epoxy resin
By chemical structure, epoxy resin is a synthetic oligomeric compound. Epoxy materials are in demand in almost all spheres industry. In free form, epoxy resin does not apply. It manifests its unique properties only in conjunction with the hardener after the polymerization reaction.
When combining different types of epoxy resins and curable substances, completely dissimilar materials are obtained: solid and hard, stronger steel and soft, like rubber. Epoxy resins have resistant to the effects of acids, halogen, alkalis, dissolve in acetone and esters without film formation. The cured epoxy compositions do not distinguish between volatile substances and differ in a small shrinkage.
What is hardener
Epoxy composition includes two components. When mixing, they enter the polymerization reaction. The polymerizing component is called a hardener.
By various combination of resins and hardeners, a wide variety of epoxy compositions are obtained.
Phenols, tertiary amines and their analogues are used as curing agents. The ratio of epoxy resin and hardener has extensive limits and depends on its composition. Epoxy resin is a reactor, the reaction of the interaction of epoxy resin with a curing agent is irreversible, this means that the frozen resin does not dissolve and is not melted as thermoplastic.
What should be the ratio of resin and hardener
The excess and lack of a hardener in epoxy composition is negatively affected by the quality of the polymer: the strength, heating resistance, potent chemicals, water, is reduced. With a lack of hardener, the product becomes sticky due to unrelated resin. Excess the loose hardener is gradually released on the surface of the polymer. For different compounds, the resin and the curing component are taken in different proportions, which is reflected in the instructions. In modern compunds, the ratio of 1: 2 or 1: 1 is most common.
From what depends the curing rate of epoxy resin
There is a commodity misconception that if you take a hardener more than the norm, the curing will happen faster. The easiest way to accelerate polymerization is to increase the temperature of the reacting mixture. An increase in temperature by 10 ° C accelerates the process by 2-3 times. There are special compounds containing curing accelerators, as well as epoxy compositions that can be bought at low temperatures. The temperature of the mixture and the type of hardener are the main factors of influence on the curing rate.
Advantages of epoxy resin
Epoxy resin has significant advantages over similar materials:
- high adhesive strength,
- minimum shrinkage,
- minor moisture permeability in cured form,
- high resistance to abrasive wear,
- the best physicomechanical parameters.
Types of epoxy resin
The curing temperature of the epoxy resin varies from -10 to + 200 ° C, depending on the type of composition used. Cold and hot curing resin distinguish. Epoxy resin and cold-type hardener is used most often in everyday life, in production with low power and where heat treatment is not allowed. For the manufacture of high-strength products capable of withstanding heavy loads, high temperature and active chemicals, apply a hot-type curing components. With hot curing, a more dense mesh of polymer molecules is formed. Epoxys and compositions are developed, which are frozen in conditions of a wet environment and even in sea water.
Where epoxy resin is used
Epoxy materials are widespread all over the world from the middle of the last century.
In recent years, the nature of their application has undergone significant changes, but remains traditional use in the following areas:
- For the impregnation of fiberglass or glass. As an impregnating means for fiberglass and for gluing parts, epoxy compositions are used in electrical engineering, radio electronics, automotive and aviation industries, in the production of fiberglass in construction, ship and mechanical engineering, in workshops to repair boat buildings and body elements of the car.
- Coatings for waterproofing. Epoxy resin has found an effective use for waterproofing floors and walls of basement and pools.
- Chemically resistant coatings. Paints and materials for the inner and exterior decoration of buildings. Impregnations to increase the strength and waterproofing of porous materials: concrete, wood and others.
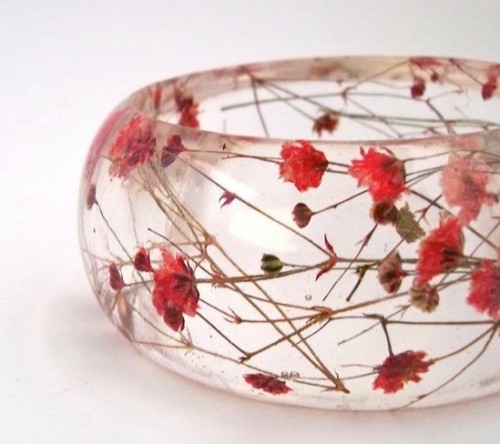
- The transparent solid material obtained by the fill in the form with subsequent machining, by cutting and grinding. It is used for the manufacture of fiberglass products in the construction, electronic industry, designer work, and household.
Preparation of the surface for applying epoxy resin
Regardless of the type of surface, with applying epoxy composition, it is necessary to comply with a number of rules for high-quality adhesion (sticking):
- Degreasing. On the surface there should be no traces of fat and petroleum products. The surface is usually purified using effective detergents or solvents.
- Lack of gloss. The thin top layer is removed by grinding. Small surfaces are prepared by manually emery paper. Large areas are treated with grinding machines, the resulting dust is cleaned with an industrial vacuum cleaner.
- In the manufacture of layered fiberglass or layered laying of bulk epoxy floors, paints and varnishes, each next coating is applied to a non-fully frozen and still sticky previous layer.
- If it allows technology and requirements for the finished product, then the substrate (bottom layer) is sprinkled with small sand, after curing, the extra sand is removed and a new layer is applied.
Epoxy adhesive
Epoxy resin especially well shifted its properties and gained widespread use as glue.
Properties and Application of epoxy glue
It is epoxy resins that are most suitable for creating protective layers or bonding materials with a non-porous surface: aluminum, steel, tick, oak, eucalyptus and other dense wood, ceramics, faience.
Special epoxy compositions with durable adhesion to many materials are used as universal adhesive. Their end properties after curing vary in a large range. Adhesive compositions are elastic and tough. For work in household conditions, formulations that do not require accurate observance of the resin proportion to the hardener are manufactured. It ranges from 100: 40 to 100: 60. This composition includes a cold type hardener.
Epoxy glue is considered one of the most universal and reliable means, due to the high-quality adhesion and connection strength. It is used to glue parts in various fields of activity, starting with shoe workshops and ending with aircraft.
How to cook epoxy glue
To obtain glue, epoxy resin is mixed with a hardener in small quantities (several grams) at room temperature. Standard proportion of epoxy resin and hardener - 1:10. Accurate compliance is not required. Admissible overdose of the hardener to 1: 5. A small amount of resin and curing agent are mixed manually.
How to prepare a large volume of epoxy resin
The ignorance of the specific properties of the epoxy resin leads to problems in the manufacture of a large amount of resin with a hardener. The greater the amount of epoxy material, the stronger it is highlighted. If the epoxy resin with a hardener is not calculated for mixing in large quantities, then immediately after the connection, the mixture is instantly polymerized, it becomes dense and unsuitable for further use. In the worst case, the mixture boils, the caustic smoke stands out, self-burning occurs. This is due to avalanche-like resin warming, which speeds up the polymerization reaction and causes even more intensive heat generation.
When buying an epoxy resin and hardener, you should clarify and consult a specialist for what purpose it is intended. From a special composition for a large volume, it turns out clean, transparent, without air bubbles and evenly frozen casting.
The production technology of a large volume of epoxy composition, for example, several kilograms, differs from the mixing of several grams of glue. Before adding a plasticizer and hardener, the resin is heated to reduce viscosity. Sometimes the resin with long-term storage becomes viscous or crystallizes and turbulent. To eliminate these phenomena, the resin is heated in a water bath. The tank with the resin is lowered into the water and heated to a temperature of 50-60c.
It should be known that an increase in temperature by 10 ° C accelerates the polymerization reaction by 2-3 times. When boiling, epoxy resin foams, becomes muddy white. Such a composition is not suitable for use. Sometimes solvents and diluents are added to reduce viscosity. Even a small concentration of the solvent (5-7% of the total volume) leads to a pronounced reduction in the strength and heat resistance of the product. Subsequently, any diluent "comes out" from the polymer, which entails an even greater deterioration in the quality of the material.
It is necessary to completely eliminate the presence of water in epoxy resin and hardener. As a result of water from entering, epoxy resin becomes muddy, loses its properties. Currently, water-fused epoxy resin is available. Such formulations are specifically bred by distilled water to obtain a dispersion.
The process of mixing the components of epoxy material starts with the addition of plasticizer. A mixture of epoxy resin with DBF is slowly heated, with the use of DEG-1 - simply mixed. For more thorough mixing, a building mixer or a special nozzle on a drill is used. The proportion of epoxy resin and the plasticizer is selected depending on the required plasticity, but most often the proportion of the plasticizer is 5-10%.
A hardener is added to the epoxy resin mixture with a plasticizer. It is advisable to cool the epoxy resin to 30 ° C to prevent the mixture boiling. Standard resin proportion with hardener - 1:10. Sometimes in specific technological conditions, the ratio varies greatly from 1: 5 to 1:20. For uniform dissolution of the hardener in the resin part, constant mixing is necessary. Otherwise, curing will be heterogeneous and unrelated hardener will continue to joke. For a high-quality mixing, the hardener is poured gradually, very slowly thin flowing, with constant stirring of the resinular part.
Even a temporary increase in the concentration of the hardener in a part of the tank leads to "boiling" epoxy resin. The resin becomes matte and covered with foam and as a result is not suitable for use. For a large volume of several kilograms, you will need a drill with a special nozzle and low revs. The reaction of the epoxy resin compound with the hardener is exothermic, with heat release. Sometimes when adding a hardener, the epoxy resin is too rapid and almost instant solidification. This is due to the overdose of the curing component and the elevated source epoxy resin temperature.
What is "lifetime" epoxy resin
The "life time" epoxy composition is called a period of time, during which the composition retains a liquid or viscous state after connecting the resin with a hardener and is suitable for processing. "Lifetime" is different from different types of resins and hardeners. Compositions that are cured at -10 ° C are produced, and there are from + 100 ° C and higher. A mixture of resin and hardener is suitable for use usually for 30-60 minutes, which depends on the temperature of the resin, the form and quantity of the hardener.
How to make bulk products from epoxy resin
The manufacture of a large epoxy resin has certain difficulties. It should be transparent, without air bubbles. Curing in the thicker and on the surface should be uniform. If the thickness of the product is more than 2 mm, the material is usually applied by layers after the primary polymerization of the previous coating.
Epoxy resin can be poured into forms. So that the finished product is easily separated, the shape is lubricated with technical vaseline or other fat. With the help of a powder dye, any color attaches. After the work is completed, the product is first kept at a temperature of a bit above room. After 2-3 hours, the primary polymerization occurs, curing "to the digit", after which the product is heated in the roast cabinet to accelerate the curing process to 5-6 hours.
At room temperature, full polymerization lasts up to 7 days, and when theta is added (triethyleneteremin), the surface may remain sticky.
The product cast from epoxy material is further to be machined (cutting and grinding).
Epoxy resin domestic production is unsuitable for casting massive products due to uneven curing thicker.
How to give an epoxy resin color
At home, it is difficult to prepare the painted epoxy composition of a specific color. In order for the pigment evenly distributed in the resin and after curing it turned out a high-quality surface, manufacturers are used in non-ferrous epoxy compositions of dozens of different surfactants (surfactants). It should be remembered that pigmented reduces the transparency of the resin, sometimes darkens or changes the color. Pigment is added to the catalyst, but after wax.
With which you can combine epoxy resin
Epoxy formulations are used with woven materials to enhance adhesion strength in hard operation, but high cost limits their widespread use.
A combination of epoxy resin with other types of resins is possible, for example, with polyester. The main rule during combinations of different types of resins - they should not be contacted in liquid and non-dedicated form. The liquid epoxy resin is applied over the frozen polyester layer. With reverse combination, the polyester resin on epoxy coating is poorly held. If it is necessary that such a sequence of application is necessary, then the cured epoxy surface is cleaned with sandpaper or wipe with solvent. This will achieve the highest possible adhesion.
Safety rules
In an uncured, epoxy resin is dangerous to health. Maximum precautions must be taken, especially with respect to amine hardeners.
Many epoxy compounds are able to cause dermatitis, skin burns, the defeat of the respiratory organs.
When working with chemicals it is very important to strictly comply with the safety rules:
- You can not use dishes designed for storing and cooking.
- Working with epoxy resins is allowed to be carried out only in overalls, gloves, with protective cream. When grinding cured products, glasses and respirator are sure to wear.
- The epoxy-diain resin is stored in a tightly closed container at a temperature of no more than 40 ° C. Shelf life of 12 months.
- If the epoxy resin appears on the skin, it is immediately washed with water with soap or wipe with denatured alcohol.
- All operations with epoxy should be carried out in a room with supply and exhaust ventilation.
Characteristics Epoxy Resin ED-20
By chemical composition, epoxy resin ED-20 is an oligomer based on Diglycidyl ester diphenylolpropane.
For curing dialan epoxy resin ED-20, various substances are used - aliphatic and aromatic amines, polyamides, polycarboxylic acids and their anhydrides, phenol formaldehyde resins and other connections. Depending on the type of a curable agent, the characteristics of the ED-20 resin vary widely.
- ED-20 is used in industrial production and in its pure form, and as part of composite materials: filling and impregnating compounds,
- glue,
- sealant
- reinforced plastic
- protective coatings.
Epoxy resin ED-20 is not explosive, but burns in the source of fire. Contains volatile substances (toluene and epichlorohydrin) in microscopic doses. According to the degree of impact on the human body, these compounds refer to the 2nd hazard class.
Epoxy Resin Quality Standards
When buying an epoxy resin, especially large volumes for large-scale work, it is necessary to check the characteristics for compliance with quality standards according to GOST. For example, high-quality indicators of epoxy resin ED-20 of the highest grade according to GOST 10587-84 include:
- Appearance - highly viscous transparent without mechanical inclusions and marks of water.
- Color by iron-roll scale - no more than 3.
- Dynamic viscosity, at 20 ° C - 13-20 Pa * s.
- Gel time with the hardener - not less than 8.0 hours.
- Also provided normal contents of various chemical compounds: mass fraction of epoxy groups - 20,0-22,5% chlorine - not more than 0.001%, saponifiable chlorine - not more than 0.3%, of the hydroxyl groups - not more than 1.7%, volatile substances - not more than 0.2%.
The package for epoxy resins - steel buckets, drums and barrels.
epoxy cost ED-20 of 140 to 220rub / kg depending on the volume of the packaging container.
The use of epoxy resins for the protective coating of timber
Epoxy timber serves to create a waterproof barrier and maintain a stable moisture level. The most common epoxy protection is applied in the manufacture and repair of boats and yachts. For wooden boats used plasticized epoxy resin, which has sufficient flexibility and elasticity. This feature allows you to handle the details on the table, and then installed on the hull of the boat. The resin is mixed with the hardener in the desired proportions and carefully laid evenly first squeegee and then foam roller.
Once the surface ceases to stick, the next layer is applied. For greater reliability, gluing each layer recommended manually sanded with sandpaper or a sander. Grinding topcoat Scratching can be replaced, the removal of the fine epoxy resin chips. Epoxy is a good base for varnish. At the end of two lacquer layer is applied. It is undesirable to work in bright sunlight
Applying epoxy resin to impregnate glass cloth
The outer surface of the hull or boat often coated with epoxy resin reinforced with steklotkannym. Such a coating has a high wear resistance, water resistance, standoff bumps. Regardless of the type of glass and the type of resin gluing process is not difficult, you just need to glue fabric to the surface. The main task - not to allow excess epoxy. For this:
- Pre-applied resin layer.
- After curing, the sealed cavities resin mixture.
- Align the tabs and nodules.
- Dust wipe clean with a damp cloth.
- Fiberglass cloth is rolled over the surface.
- Fix it masking tape.
Should not be diluted too much resin and hardener, quite half a kilo, the estimated consumption of 300g per square meter If the surface horizontal, the resin is simply poured onto the coating zigzag lines and partitioned rubber spatula, the inclined surface is treated with a roller. For uniform distribution of resin strongly adheres extrusion and air bubbles adhered fiberglass tested again clean the platen. When the coating is hardened a little, the excess glass is cut with a razor.
Durability for ages
Recently appeared on the market many new epoxy compounds, an even more efficient and safe. Epoxies successfully compete with traditional materials: wood, metal, ceramics. Epoxy resins are more durable, long lasting, resistant to corrosion. In epoxy great future and limitless application possibilities.
New comments
Add a comment
To send a comment you need authorize.
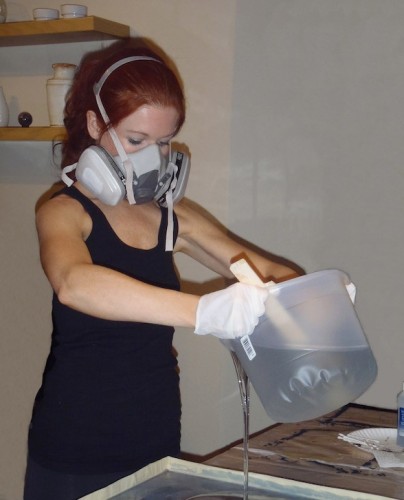



































There's a girl in the photo with raspiratorom. What can interfere with resin in such quantities?
good skilled worker a respirator!)