How to translate a tree Useful advice,Plot.

Many gardeners face the need to transplant trees. This simple case requires some effort and experience. However, if you adhere to some rules and recommendations, even a novice gardener will be able to transplant trees.
Content
When you can transplant trees
For a successful transplant, it is important to keep the root tree of the tree. In addition, you should try to create all the necessary conditions so that it takes place in a new place. Adult fruit trees can be transplanted at any time of the year, but still there are some recommendations:
- So, in the spring it is better to do before the start of growth, in the fall during a mass leaffall.
- In winter, it is better to transplant when the air temperature holds at a mark not lower than the mark -5 degree.
- The most optimal time for transplanting trees in medium latitudes is considered early spring.
It is important that the fruit trees to be transplanted are not over 20-24 years old. At the same time, some features of varieties and species should be taken into account. So, trees that early begin fruitful fruit, should be transplanted only if their age is less than 19-20 years.
For decorative varieties and species, it is important that the trees that are selected for transplantation were healthy and developed normally. They should not have damage to the branches or post. Therefore, the trees in which the heap is formed to transplantation.
How to transplant a tree: several ways
There are the following techniques for transplanting adult decorative and fruit trees:
- With soil lump.
- With attached roots (without a coma).
- With preliminary preparation of trees for transplant.
Tree transplant with land
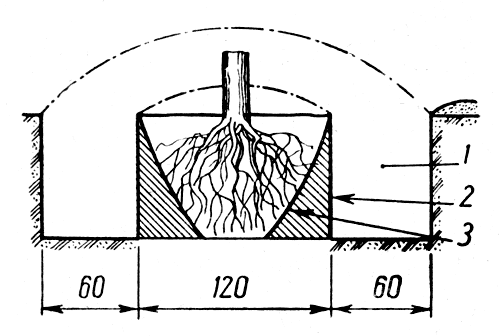
Most often use a transplant with soil com. If you used to transport trees with an earthen room, it was quite difficult, then modern technologies are much easier for this business. The older the tree, the more it turns out the root system in size and, therefore, an earthen com. So, those whose age is 7-9 years old, have a diameter of 1-1.5 m. In those who are from 10 to 14 years, an earthen one about 1.5 meters. And the older trees in diameter reaches up to 2 meters. The height of the coma is set to the depth of which the root system can be sought. For example, for an apple tree, this value is 65-75 cm.
An earthlom may have a form of a cylinder or cube. It depends on his form, how the tree will be painful. Accordingly, if it is to have the form of the cylinder, the tree is in the circular, and if the shape of the cube, then make a square ditch, the dimensions of which are 40-45 cm.
If roots are emerging during the digging process, they are usually trimmed with a garden knife at one level with a coma wall. Thick shoots can be chopped by an ax, a shovel or cut with a hacksaw. Only in the latest cases for faster roots for faster root, they should also be cleared with a knife to get a smooth surface.
In order to be more comfortable to sabe off and pull out of the pit, one of the walls of the ditch can be made inclined. If the tree is transplanted from a loose scattering soil, then the better after digging is to stripped with a lodge, wire mesh or boards. The same is recommended to do if the tree should be transferred to a large distance for transplantation. If the kom has a round shape, then it should be put on the boards vertically and strung the wire. The root system in the form of a cube with sides and from the bottom is cut by boards, which are bolted between themselves. The trim in the size of the bottom and sides of the coma in the form of a collapsible box can be made in advance.
The lower part of the coma can be trimmed with a solid wire that throws around the root system in the form of a loop. At the same time, both end of the loops are attached to the tractor, which when moving will pull the wire and thereby cut off the soil under the lower parts of the coma along with the roots.
Next, the land comes should be carefully removed. To do this, an iron sheet is used to which the tree along with a coma is pulled out of the pit along the inclined wall. For this, there are still special winches, cranes and other tools.
For transplanting adult trees, several fixtures are used in sites and gardens:
- So, shovels are used to dug soil coma.
- The axes are needed to hide the roots.
- For lifting wood from the pit, logs are used, rollers and tripods.
- Iron sheets apply for movement.
Transfer and preparation for transplantation
If you need to translate trees for long distances, then before loading on transport, the branches should be associated. In addition, the trunk and crown wrapped with a lot. Trees in the car body are placed as follows: the side with the soil lump should be near the driver's cab, and the trunk in the inclined position. If some trees branches are too big, then they are not damaged on the side of the car, there is a tarpaulin or a rogger. If you need to translate for a short distance, the tree can be installed in a vertical position, and to secure with solid ropes.
Adult trees get out of the body with a lifting crane. For this purpose, you can also use inclined boards or logs. It is advisable to do it directly to the pit prepared in advance. Its dimensions must be somewhat larger than coma size. After landing between the coma and walls of the pit, there is usually enough space to fill it with nutrient soil and fertilizers.
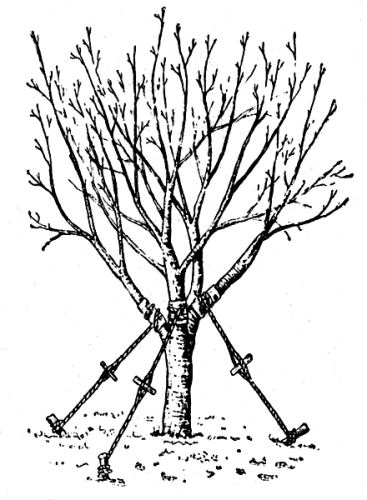
It is important to plant a tree on the same depth on which it grew before. It should be noted that the soil comes after landing can settle. In addition, it is desirable to place it in such a way that the ratio towards the sides of the light is preserved. Appropriate marks are recommended to apply a tree to the trunk even before it is dug. To do this, use paint or chalk. This mark will help set the tree in a new place correctly. The soil, which is filled with the space between the pit machines and the soil lump, is slightly condensed. After landing, the tree in a new place should be strengthened using additional supports, for example, durable stretch marks from the wire. After the work is completed, the tree must be abundantly pouring.
Transplantation
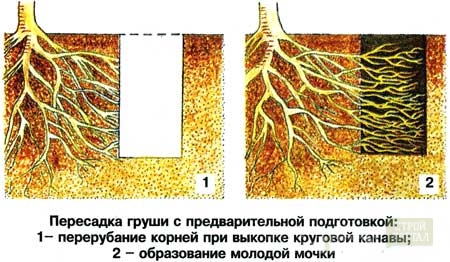
This is another way of transplanting trees, which requires more time than the previous one. Its meaning in the following:
- In the spring around the tree digs a ditch round or square shape.
- Then it is filled with a fertilized soil.
- After that watering.
- Leaves until spring.
- As a result, at the ends of the cropped root system, the formation of young roots, which grow well in a fertilous land.
- In the spring tree digs. At the same time, it is important not to damage the formed roots. Therefore, the ditch is digging a large size. This approach allows you to make a transplant less painful. In addition, it improves the adherence of the tree in a new place. The rest are the same works that were described above.
Tree transplant without coma
In this case, the root system is not so truncated, as when transplanting with an earthen room. At the same time, it is important to protect the roots from drying.
Transplant steps in this way:
- In order to dig a tree, the distance equal to the length of the roots retreats from its barrel, and dig a ditch to a depth of about 1 m.
- After that, carefully remove the top layer of the soil until the roots appear. Then they are freed from the ground with the help of a cola or water, watching they do not damage. The top layer of the soil is referred to the dug ditch.
- Called roots need to wipe wet moss, grass or moisturized burlap. As the roots are reaping, the tree will become less stable. Therefore, it must be secured with wire stretch marks.
- If the tree needs to be transported for a long distance, then branches and roots bind and pack. As for the conditions for transportation and planting the plant in a new place, then they are the same as when transplanting in the first way (with a land com).
- Obviously, the transplanting of trees without a coma is more convenient for at least the fact that they are easier to come from the pit. The same can be said about loading and unloading. The main difficulty is the liberation of the roots from the Earth, which requires great care and care.
Care of transplanted trees
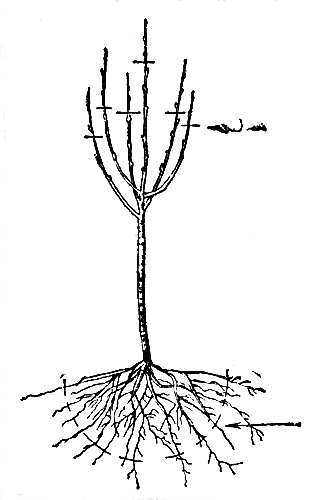
The tree after the transplant continues to evaporate moisture through the pores of the branches and the trunk. In this case, due to the loss of part of the root system when digging in a new place, it gets already less moisture from the soil. This can cause drying the above-ground part or even the death of a tree. To avoid this, before or after a transplant, skeletal branches should be shortened by about 1/3. You can swift the crown, deleting some shoots. At the same time, it is desirable to remove a couple of large branches, not a lot of small.
The available wounds should be painted with oil paint on a natural olife or to deceive the garden boraner. The barrel and the lower parts of the skeletal branches in order to prevent excessive evaporation of water, it is necessary to assign agencies, moss, burlap or straw harnesses. In the summer, a tree, or rather the soil under it, you need to periodically moisten. After transplanting, it is useful for all branches with a lime solution. In summer, the foliage can harm the spiders and silkworms. Therefore, you need to follow this, and take the appropriate measures in a timely manner. Flowers that were formed in the first year cannot be left. Therefore, they are broken.
How to transplant a young tree
General rules
Young trees to transplant more difficult than adults. There are several important nuances. Basically, the principles of transplanting young trees are no different from other plants.
For transplant you need:
- Shovel.
- Wank or plastic canvas.
- The source of moisture for watering, for example, a container with water.
- A small healthy seedling.
The transplant takes place in several stages:
- First you need to choose a suitable seedling. Its root system should be such that the plant is easy to put in the ground. Therefore, it is better to take a small sprouts. The seedling of the tree should be good to transfer a transplant. True, it is not always possible to learn before landing. So, it is known that the transplant is well tolerated by Oak, Magnolia, Birch, Eucalyptus, Tea Tree and Kizil.
- When a seedlock is selected, you need to prepare a place to land. In order for the tree to take root, new conditions should be similar to those that it is accustomed. That is, you need to observe the soil moisture, the intensity of solar radiation and the way of removal of water.
- The selected place pumps the fossa of suitable size. Its depth depends on the dimensions of the root system. Roots must settle down at the same depth that was before. If the soil is too dense, then in this case it will be necessary to dig a pit of a larger diameter. Otherwise, the roots will not be able to break through.
- As for the fertilizer of planted seedlings, it is usually not done until they come down. If this rule is not respected, it will lead to an accelerated growth of the plant, which, in turn, will be a heavy burden on the roots.
- After that, you need to dig a seedling. To do this, first, you should take an acute blade with a rounded edge, with the help of which notice at least 280 mm the edge of the root tree of the tree. This is likely to ensure that the shovel does not hit the root when digging.
- Then, on the planned line of the blade with an effort is immersed in the ground, as deeper. If the soil is too dry, then it is best to moisten it first. With a wet soil, the tree can be digging, not hit the roots. If there is a lot of sand in the soil, it will require a special device (retainer), allowing to keep the roots of a seedling in the transplant process.
- Now carefully pull out a dug-out tree from the ground. To do this, take it for the base of the trunk and raise the seedling up. If the transplantable plant has big roots, then it will have to dig up enough long. In any case, you should not apply great effort to pull the tree from the ground. Otherwise, you can damage the root system, which will complicate its transplantation.
- If there is a lot of roots in the soil, then such a tree should be transplanting near the place where it was dull. If the seedling is required to be transported to another place, you can take a package or flap of fabric and put a tree with roots into it. It should be known that different manipulations with the root system, including the fall of the tree during transportation, can badly affect the survival rate of the seedling in a new place. The fact is that after the release of the roots from the Earth, the air dries them.
- The dug seedling is planted into the prepared hole. It is important to make sure that he will enter the same depth as he was in the same place. When the plant is already placed in a hole, you should take a shovel and break the earth around it. It should periodically water the soil with water. This will help avoid the formation of air bubbles. The most important thing is not to moisten the soil too much, otherwise water can wash off with the roots of the useful soil.
- Now you need to fill the hole of the dug soil and dissolve the soil. The remaining soil can be used to pour shaft around the base of the barrel. It will not allow water to immediately spread after irrigation. The height of the embankment of 8 centimeters will be quite enough.
- When water is absorbed, the tree should be pouring again so that the soil is torn. From above it is allowed to add some more wet soil.
It remains to strengthen the seedling with reliable supports. This is especially true if there is a possibility of a strong wind that can bend a tree. To secure the plant into the ground at a distance of 850 mm from the trunk, you can insert the iron bar, a wooden pitch or a pipe. After that, at the bottom, tie them to the tree rope. This is necessary for fixing the plant. For the rope does not pump into the barrel, the base of the seedling is desirable to wrap something, for example, a garden hose.
Tips on transplant
- When is it better to transplant trees? It is recommended to do it late in autumn or in winter, i.e. Then when the tree is in a nozzle state. If you managed to dig it together with the soil on the roots (with a lore land), then in this case it should normally take care even when transplanting in the summer.
- Before digging a tree, it is advisable to note which side to the sun it was planted earlier. This should be considered in a new place, i.e. The plant must be installed in the same position as before. This will allow a seedling quickly and easier to take care. To note the side directed to the north, you can, for example, tie a ribbon to branches on the north side, then put in a new well so that shoots with ribbon also indicated north.
- If the tree will lose leaves after transplantation, then you should wait a bit to grow new. Foliage's dejunation is most often a consequence of stress that is for the plant is a transplant. This can occur even with healthy trees. If the branches after the transplant are still smooth and flexible, it means that the tree most likely survived.
- Watering a tree in a new place in the first season is preferably no more often than once a week.
- Most often, the transplant is successful, but this fact does not mean that after that the tree does not need appropriate care and attention. When a seedling in a new place will begin to grow, fixing ropes should be removed.
- The resulting hole after digging the tree should be filled with the earth, so that no one can fall there by negligence.
Cautions:
- You should carefully choose a tree for transplantation. So, if you want to plant a new plant on your site, then it is not worth digging out trees from the ground that has the owner. Especially if you do not have permission. In addition, you should not invade private possessions and parks in search of trees. In many countries, this is considered a violation of legislation.
- If you are looking for a tree in the forest, then you need to protect yourself in advance from forest insects that can carry dangerous infectious diseases. In addition, wild bees, OS, bumblebees and harnesses should be watched. Some wild animals and snakes may be dangerous. There are often hazardous plants in the forest, for example, poisonous ivy.