Gasilicate blocking technology Building materials

Aerated concrete is a modern building material that has a number of benefits compared to traditional brick, stone or bar. Laying gas silicate blocks is much faster and easier than the construction of buildings from other materials. However, with all its simplicity, the process is not devoid of a number of features that you need to know for the successful outcome of the case.
Content
General characteristics
Description and properties
The main advantage of aerated concrete is its ease with fairly large block sizes. This allows you to significantly reduce the timing of the walls. A small weight does not squeeze a solution from seams, thereby simplifying the subsequent finish.
Unlike the walls of the brick, the walls made of aerated concrete can be built without pauses. Various special fixtures for laying gas-silicate blocks such as a toothed spatula, a rubber pin or special buckets greatly simplify work with the material.
Impact moisture
The degree of moisture of aerated concrete is subordinate to the constructive features of the walls, as well as the time of year. The higher the percentage of humidity, the faster the material will be unusable. So that the material does not absorb moisture, it is necessary to ensure proper waterproofing and ventilation of the room.
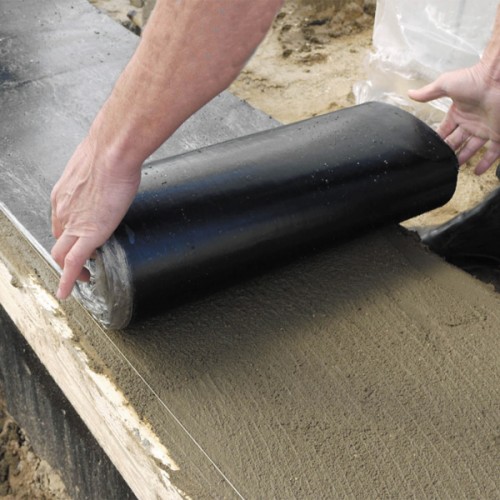
The rubryoid or waterproofing film is perfect as waterproofing.
Advantages
Aerated concrete has a number of undeniable advantages over other building materials:
- low weight of blocks with rather large dimensions;
- durability;
- high-quality heat insulation;
- noise insulation;
- the absence of "cold bridges";
- strength;
- the smooth surface allows you to save on the inner and external finish;
- installation elementality;
- the price of laying gas-silicate blocks is lower than construction of brick or timber;
- ecology.
Gasilicate blocking technology
First row
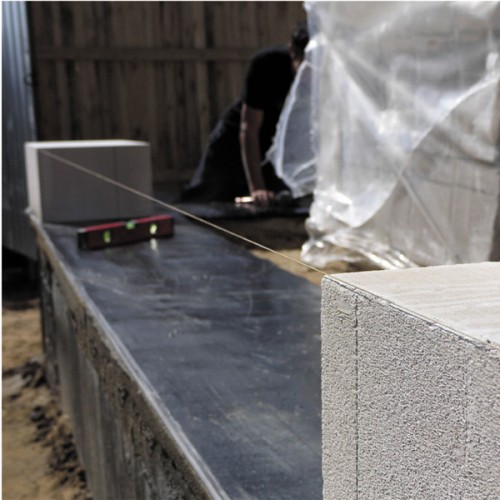
Laying the first row of gas-silicate blocks is carried out only after careful preparation of the base. To do this, it is necessary to mount the cut-off horizontal waterproofing from the rubberoid or any rolled material (bitumen or polymer). It is necessary to align the surface with a cylma or a comb, and on top of the waterproofing, put a solution from sand cement (1: 3). The final stage is a horizontal assessment using a building level.
The first row in the masonry is the most important, so it should pay special attention. The strength, appearance and durability of the structure will depend on the correctness of the masonry. It is necessary to constantly control the horizontality using the level and plumb. Align the blocks are recommended for rubber Cyans.
The electrolovka, as a tool for laying gas-silicate blocks, will help if you have a gap in the end of the first row, the size is less than the length of the standard block. However, it is easy to "fit" the unit under the desired size can also be a conventional manual saw. After dipping, the surface is leveled by Halfury or the plane.
Masonry solution
Many experienced builders prefer to lay aerated concrete for traditional cement-sandy solution. Some come so for the considerations of savings, others - by habit, but the cheapness of the solution is only an illusion. His expense in the process will make all new and new portions, while the laying of gas silicate blocks can flow much faster and more economical.
Glue for aerated concrete costs more than a conventional cement solution twice, but its consumption is much smaller. One part of the glue or six parts of the solution is spent on one square meter of masonry, because the economy of the traditional solution is considered illusory.
The correct form of blocks and the use of a special adhesive composition allow you to prevent the occurrence of "cold bridges". Elements are clearly adjusted to each other and fit as thick as possible, excluding any possibility of the appearance of drafts, condensate, heat loss and mold.
Technology laying gas silicate blocks involves the use of only specially intended glue. The use of a conventional cement mortar Many professionals consider a gross violation that can lead to rapidly damage material and significantly reduce the operating time of the room.
Regardless of the shape of the used blocks, the glue must completely fill the seams. The compound of inter-block seams, which is happening on the principle of "comb-groove", remains partially unfilled glue.
The thickness of the seams should not exceed 3 mm. If you have to build a house during the cold season, it is recommended to add antiorrosic components to the adhesive solution to eliminate the occurrence of evillites.
How to work with glue:
- Divide the adhesive solution to the consistency of thick sour cream and mix thoroughly.
- Apply glue using a trowel or a special laundry with a curved side.
- After applying glue, crumple it with a spatula with teeth.
- After laying a row, align the surface of the blocks by level using a planer for aerated concrete.
- Remove the small litter and fragments of blocks with a rigid pile.
- Align the blocks after laying each row.
Continued masonry
When the first row is ready and aligned, all subsequent must be launched from the corner. To ensure maximum horizontal, install corner wooden rails. If the length of the wall is very big, you can put intermediate beacons.
Stacking gas silicate blocks (photo) must be made with a dressing, shifting each subsequent row relative to the lower minimum of 8 centimeters. The glue that will perform from the seams must be deleted, and not to rub.

Film from blocks must be removed as the installation is moving to once again not expose the material to the environment. After watching the video about laying gas-silicate blocks, you can familiarize yourself with the basic principles of work with the material.
Reinforcement
All houses, including aerated concrete, are experiencing serious loads that can deform the structure. Despite the strength and advantages of the material, it is necessary to ensure proper reinforcement of masonry from gas-silicate blocks.
To avoid cracks from bending strains, it is necessary to separate the masonry on fragments using fittings or deformation seams. To provide additional protection, it is recommended to reinforce the finishing layers of fiberglass mesh.
The method of reinforcement depends on the specifics of the future structure and operational conditions. For example, for long walls it will take a mesh for laying gas-silicate blocks, since it will be exposed to the pressure of wind loads.
Armature bookmark rules:
- Armature is laid in pre-prepared Armopoyais.
- When working with aerated concrete, the inter-row reinforcement does not apply because it disrupts the thickness of the seams and complicates the laying of subsequent rows.
- Interconnection reinforcement is permissible when using stainless reinforcement with a small cross section.

- The first row is subject to reinforcement, and then every fourth and jumper supports.
- When installing in places of jumpers and areas of window openings, it should be reinforced by 90 cm on each side.
- Deformation seams are not subject to reinforcement.
Deformational seams
Deformation seams, as well as reinforcement, serve to ensure the strength and protection of aerated concrete walls from the appearance of cracks. Determining the place of such seams for each situation is selected individually.
In what cases are the deformation seams:
- in places of height drop;
- in places of change of thickness;
- between the cold and warm walls;
- in long unmarked walls (longer than 6 meters);
- in the connection zones with other materials;
- in areas of crossing bearing walls.
The deformation seams are compacted by minvata or polyethylene. From the inside, they are processed by a special steamproof sealant, and outside - weather-resistant.
The laying of gas silicate blocks can bring real pleasure and proceed very quickly, if perfectly "hone" the basic principles of working with this building material.