Protective shutdown device. How to choose and correctly connect an RCD Lighting

In the protective shutdown, those who hold a large number of electrical appliances in the house are most in need. Protective shutdown devices are used to protect a person from a shock when failing of electrical equipment, in case of accidentally touching the bare areas of the electrical installation, as well as to prevent the fire in case of closing.
Content
Types of protective shutdown devices (RCD)
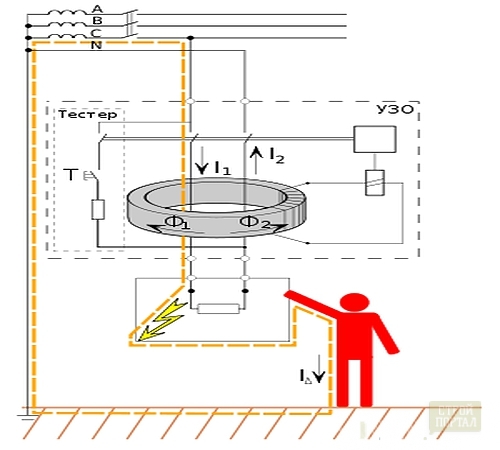
The RCD is a turning -out device that automatically turns off the electric network or part of it if the differential current reaches a certain level or exceeds it.
In order to answer the question - how to choose an RCD for work in certain conditions and not be mistaken, you need to carefully study their main types that are classified:
- by reaction to leakage current. The RCDs are divided into three varieties - AS, A, V.
AC devices interrupt the circuit if the alternating current leak increases unexpectedly or slowly. These devices are most common due to a low price and versatility.
Devices A respond not only to the alternating, but also to the prayed current that intensifies unexpectedly or slowly. Such RCDs are more suitable for dwellings. Their price is much higher than the price of AC class devices.
RCDs related to type B are used in industrial enterprises. They are suitable for any type of current;
- by the features of the rupture of the RCD chain are electromechanical and electronic. Electromechanical does not require power from the common network. They react only to the leakage current that triggers the operation of a very accurate mechanical executive system. This type of RCD is relatively expensive, but at the same time it is the most reliable, because It can function, does not depend on the volume of power.
Electronic RCD is many times cheaper than electromechanical and are more common. To ensure their work, external nutrition is required. They are less reliable, because with tension changes, their effectiveness decreases significantly. Electronic devices are not protected by all possible troubles, but from the majority, and if the funds for the purchase are limited, then this option is also acceptable;
- by speed of response. Selective RCD, triggered with a given delay (up to 0.5 seconds) make it possible to obtain protection systems consisting of several levels. Any damaged segment of the network can be disconnected separately, while without turning off the power in the entire room.
Not selective RCDs of good quality react to a malfunction in less than 0.1 seconds;
- by the number of poles. For a three -phase network, an RCD is used with four poles. They protect several single -phase networks or individual three -phase devices consuming electricity. Included with this variety of RCDs, a four -pole automato should function. For a single -phase power supply of residential buildings, two -pole devices are used;
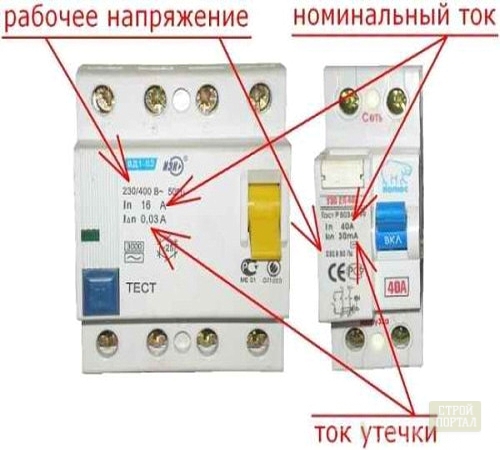
- on the current of the leak. Disabulating the residual current, under certain conditions of use, is the most important criterion that defines the working qualities of the RCD. An indicator from which you need to start, classifying them, is a current of 30 mA.
Devices that respond to smaller points of leakage protect people from shock.
Devices responding at higher leakage points are firefighter because withstand a significant load, but the residual current that they allow is a danger to a person;
- for permissible load. The indicator of the greatest possible load allows you to understand how much and what power of the electrical appliances can be powered through the RCD. When choosing a device, they usually repel from the properties of the devices connected to it. In residential buildings, most often, an RCD of small power is used-10 A. Differential RCD with the highest load of 16-32 A, are medium-power devices. Powerful are considered an RCD of 40 A and more.
By the method of preventing the closure of the RCD: there are:
- protected from super -flows;
- protected from overheating;
- not protected from super -flows.
By the type of installation, the RCDs are divided into:
- fixed, installed on a metal profile in a shield, machine guns;
- portable - installed on the extension cord;
- devices in the outlet.
Installation of RCDs and its connection
In Russia, the RCD installed in the shield is most often used. For the mains, the house is used by two -pole devices that occupy 2 places on the profile. They are placed next to the lines of protected chains. Only fire -fighting RCDs are departed from this rule next to the introductory machine.
If the electrical wiring is divided into parts, then it is best to mount one RCD at the input and several on different parts, programming the cascade shutdown of the devices. The RCD for this purpose is mounted at any lower level with a lower turnover current or with a greater speed of shutdown.
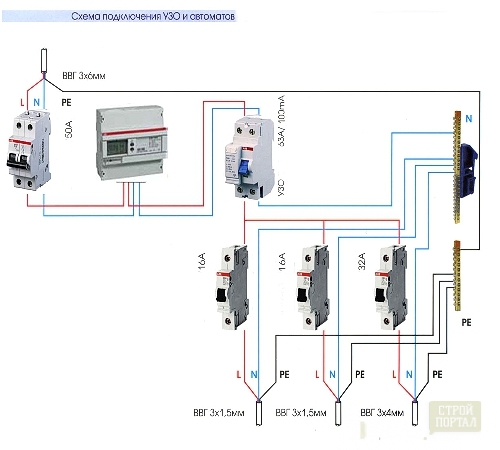
Connection of a single -phase RCD occurs according to a thought -out scheme. The connection diagram of the RCD must be developed for each power supply separately. When designing a protective system, the functions that the device will perform, as well as the properties of the network, are taken into account.
When installing and connecting the RCD, you must take into account some rules:
- in order for the device to function normally, the working zero conductor should not contact with grounded elements and a protective conductor. In the shield, there are tires for them;
- in the connection of the device, the conductor of grounding does not take part;
- power on the RCD is connected to the upper terminals;
- the neutral of the power must be connected to the connector indicated by the letter "N". This rule must be observed when using an RCD of any kind and purpose;
- the largest possible current of the device should be equal to the current of the circuit machine guns or exceed it. If you observe this rule, machine guns will protect the RCDs from overload;
- RCDs and the operation of the installed device must be checked.
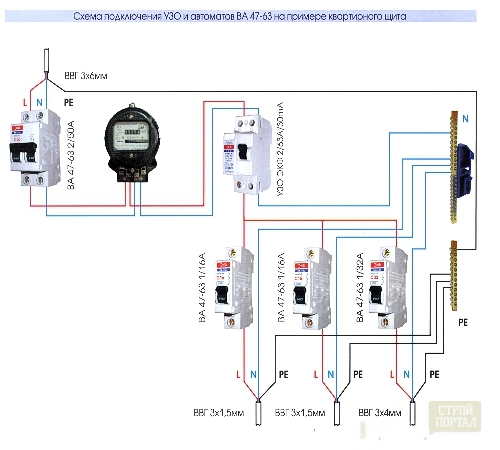
That it is better to choose an RCD or difavtomat
A difavtomat is a differential automatic switching device that responds to overload, which also includes the role of RCD - automatically turns off when differential current or leakage current occurs.
Comparative characteristics:
- the difavtomat occupies much less space in the shield;
- the installation of a difavtomat is more simple than installing an RCD and takes less time;
- when the RCD is triggered, it immediately becomes clear that there was damage in electrical appliances or in the wiring. There can be more reasons for the response of the difavtomat (leak, overload, short circuit), so to install them will have to be spent more time;
- the price of RCDs and difavtomat, although it depends on the manufacturer, fluctuates in about the same limits;
- in case of failure of the RCD, it is simply replaced by a new one. And in the case of a difavtomat, if any of its elements burned out, while others work, you still need to change the entire machine and in this case it is much more costly than replacing individual devices;
- in terms of reliability, there are no special differences between the RCD and the difavtomat. Most likely, the quality depends more on the specific manufacturer.
From the above characteristics, it becomes clear that each device has its own advantages and disadvantages. Therefore, having studied them, everyone should decide how to be, to buy an RCD or a difavtomat.