Calculation of wooden beams overlap Building materials

The correct selection of beams, the accuracy of their size is a determining factor for the reliability of the entire overlap. Wooden beams of overlappings are manufactured after the exact calculation of their length and cross section. The length of them depends on the width of the future overlap, and the section is calculated based on the installation step, the planned load and the length of the span. This article will describe some nuances of the selection of beams, the methodology of their calculation is indicated.
Content
Calculation of wooden beams overlap
Wooden beams are structural elements with carrier functions. When calculating them, the choice of material and installation is followed by the following rules.
- The length of the wooden beam overlap, their number and dimensions are determined after the measurements of the span, which is planned to be blocked with them. It is important to take into account the depth to which the beams will be entered into the walls, how they will be fixed in them.
- In the walls, isolated from blocks and bricks, beams should go to a depth of at least 150 mm (if they are made of timber) and 100 mm for boards. In wooden houses, beams are cut into the wall at least 70 mm.

- The length of the beams can be equal to the span when using brackets or corners: in this case, metal supporting structures take over the weight of overlapping and the rest of the load.

- Typically, the width of the span, which can be covered with wooden beams - within 2.5 ... 4.0 m. The maximum length of the beam from the bar or the board is 6 m. If the house project requires the use of longer beams, it is necessary to use a glued bar or providing Construction of intermediate supports (wall-partitions).
How to determine the load that will act on overlapping
The overlap transmits the beams to the load, which is summed from its own weight of the structure (including the weight of the inter-batch insulation and the tailboards) and the weight of items placed on the overlap. You can only perform accurate calculation by the forms of a special design organization. More simple calculation methods are available for self-execution according to the following scheme.
- For attic ceilings with a tailboard (not carrying large loads, but insulated mineral wool), the approval is true that a load of 50 kg is valid on average. In this case, the load on this overlap will be: 1.3 × 70 \u003d 90 kg / m² (according to SNiP 2.01.07-85 digit 70 (kg / m²) - normalized load for this overlap; 1,3 - the reserve reserve coefficient) . The overall load is equal to 90 + 50 \u003d 130 kg / m².
- If the inter-bullary insulation is heavier than mineral wool or used in thick boards, the regulatory load is considered to be 150 kg / m². Then: 150 × 1,3 + 50 \u003d 245 kg / m² - the overall load.
- For the attic to the number of components of the load factors, the mass of flooring, furniture and other interior items is added. The calculated load in this case increases to 350 kg / m².
- If the beams are part of the inter-storey overlap - the calculated load is taken equal to 400 kg / m².
Step and section of wooden overlap beams
Having determined the length of the beams and knowing the estimated load, you can calculate the pitch of the beams of the wooden overlap and their cross section (in the case of logs - diameter). These values \u200b\u200bare interconnected. To do this, enjoy the following rules.
- The optimum ratio of beam height to width ratio - 1.4: 1. Wooden floor beams whose dimensions depend on the parameters above, may have a width in the range of 40 ... 200 mm. The height or thickness of the wooden joists selected corresponding to the thickness of insulation and generally ranges from 100 to 300 mm. If used logs - their diameter is in the range of 110 ... 300 mm.
- Step laying beams is selected in the range of 300 ... 1200 mm, and also take into account the size of sheets of insulation material and a binder. In the case of the construction of frame structures step beams should be equal to the distance between the frame uprights.
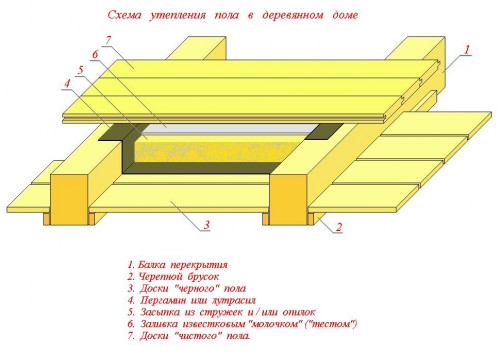
- Allowable buckling beams - 1/200 (for attics) and 1/350 - for intermediate floors. Powered overlapped relation to the length of the span.
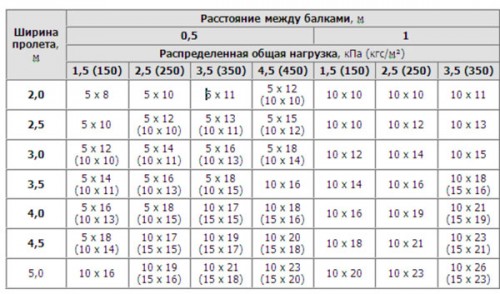
- Calculation section wooden floor beams can be made (except for the above methods), use the table of special reference books. There are also special computer programs.
For example, for the estimated load of 400 kg / m², the corresponding floors, the ratio between the pitch and span of the following sections:
- for pitch and span of 0.6 m to 2.0 m width section should be at least 75 × 100 mm;
- for pitch and span of 0.6 m to 3.0 m width section should be at least 75 × 200 mm;
- for pitch and span of 0.6 m to 6.0 m width section should be at least 150 × 225 mm;
- for step 1.0 m in width and span of 3.0 m cross section should be at least 100 × 150 mm;
- for pitch and span of 1.0 m, 6.0 m in width section should be no less than 175 × 250 mm.
Basic requirements for joists
- The beams are made of wood of coniferous trees: it has sufficient strength. Moisture content should not exceed 14%: exceeding this parameter can cause lag deflection under load.
- Not allowed wood defects, such as cyanosis, mold damage, pests and rodents.
- Before laying the beams treated with an antiseptic composition.
- The beam will be resistant to bending if its sides have a ratio of the size as a 7: 5 (for the boards).
- Flexural strength is determined lag height: the larger the value of this parameter - the greater the withstand load without bending beam.
- So that the overlap remains even under the influence of the load, the construction lift should be supplied. The ceiling of the lower tier in this case will have a small rise in the central part, but with an increase in the load on the overlap, it is leveled.
- With frequent stacking lag bars and logs allowed to replace the boards laid on the edge.

- Wood consumption will be more economical in the manufacture of beams 50 and a height of 150 ... 180 mm. The width of the laying step should be 400 ... 600 mm (it is convenient for laying insulation slabs).
In conclusion - video tutorial with a detailed presentation of the methodology for calculating the beams of overlapping and other structural elements.