Calculation of ventilation of the room: Rules and examples Climate

Installation of ventilation is absolutely necessary in any rooms, be it apartment, private house, shed, garage or warehouse. The scheme of its creation is negotiated at the building design. The house in which there is no ventilation, especially residential, will be uncomfortable, but soon and unsuitable for living, because there will always be raw and stuffy, the mold will begin to appear in the corners, the wooden elements of the building will rot, and it ultimately collapses much faster. In this article we will talk about how to calculate ventilation indoors.
Content
Why do you need ventilation
Some believe that you can completely quietly do without ventilation - our ancestors lived somehow before the invention of all kinds of newcomers. And if in the summer in such a house you can constantly open windows for airing, then in winter you will fully experience the whole "charm" of life in the old way - condensate will begin to appear on the windows, doors and walls, which in case of severe frosts will turn into a beautiful ice crust, The corners will begin to grow the gardens of black and green mold, and if you are very lucky, in a year or another we will collect the crop of mushrooms ... Is it worth saying that such a house will not have a very long time, and life in it will be a constant test for nerves and health.
With a constant insufficient inflow of fresh air, light people are starting to work worse - diseases appear that can quickly become chronic. A child growing in a house without ventilation can earn major health problems for life.
The "parade" continues constant dustiness and crying - if fresh air does not come to the room, then everything that is brewed in it is fried, dust, it is cleaned, settles on the walls and furniture with a thick layer of plaque. On a kitchen ceiling, after six months it will be possible to notice an extensive yellowish stain over the stove - these fat evaporation dated and absorbed into the plaster, for they have nowhere to go. In the bathroom on the ceiling and in the corners, eloquent evidence of the lack of ventilation in the form of mold spots due to constant humidity will also appear.
And finally, it should be taken into account that at least once a year in the house someone sick - cough and sneezing microbes are instantly scattered around the room, settled on furniture, wallpaper, curtains, carpet. Hospital chambers are raised several times a day not just like that, and now imagine what atmosphere you will find yourself after the year of life in an apartment where there is no regular air tributaries. We hope we led weighty arguments in favor of the need for a system of ventilation of residential premises and now you can go from words to business.
Checking the work of ventilation
It happens that some of the above "symptoms" are manifested even in ventilated houses. This may mean that the system works weakly or ceased to function for any reason. To check whether the ventilation works, burn the match or lighter and bring the flame to the ventilation hole - if the fire leaned towards the grid, covered the hole, then there is a traction, and everything works. If the changes did not follow - the ventilation canal is either blocked or clogged with leaves. In the case of apartments, this very often happens if the neighbors made redevelopment and blocked the air duct.
It also happens that the thrust is present, but with breaks, and at the same time it can bring relaxes from the neighbors from above or below. In this case, it will be necessary to equip the ventilation hole with the check valve, or install the automatic blinds that are closed when reverse.
Types of ventilation systems
All ventilation systems can be divided into categories depending on the functional load, the method of moving air masses and what leads them in motion.
Depending on the functional purpose, the following ventilation systems are:
- Supply - Fresh air from the street constantly enters the room.
- Exhaust - air is output from the house along the ventilation channels.
- Recycling - systems displays spent air and at the same time "pumps" in the house of fresh.
If you think about the principles of the work of the above systems, the question is subject to: "And at the expense of which the air moves to leave or penetrate the room?". To do this, use the sorting of ventilation systems by the nature of the awakening of the air masses. These sources can be natural and mechanical (artificial).
In systems with natural ventilation, air is moving due to pressure drops. You will immediately understand what we are talking about, if you remember the ventilation holes in the kitchen and in the bathroom, which is in every high-rise building - warm air and steam (shower, wash, cooking) falls into this hole and draws outwards due to pressure and gravitational forces .
In systems with mechanical sources of awakening, air is driven by means of exhaust fans that take it out of the room, acting on the principle of conventional kitchen exhaust.
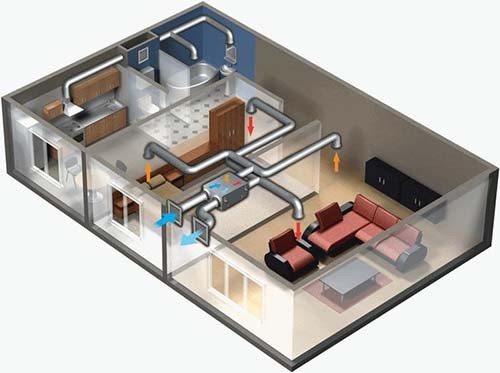
So, when the air masses have gained the ability to move, they should provide a safe and directional output (input). In this regard, another classification was developed by the method of movement of air flows - channel and non-vacant. With a channel system, it is more and less clear - the air flows through special removals, and when it does not leave the room, it leaves the room or penetrates it through the axle window openings, doors, cracks, etc.
Calculation of the ventilation system
To ensure high-quality ventilation of the house, it is only enough to choose any system you like - it is necessary to find out how much air will be output from the premises, and how much fresh air should be supplied from the street. Speaking otherwise, you should find out the optimal air exchange at home, and on the basis of this data to select the ventilation system, buy fans of certain power, channels, etc.
There are many ways to calculate the ventilation of the room, for example, to remove excess warm air or evaporation, dilution of pollution and so on. However, they all require professional knowledge and experience. We also need such a method that every owner or hostess could take advantage. To begin with acquaintance with special regulatory documents, which are designed for each state or region (GOST, SanPiN, DBN, SNiP). In them, you will find information on the requirements for ventilation systems for any premises, the necessary equipment, its facilities and location. By and large, there is everything you need to know to select the system.
But the architectural features of buildings dictate their conditions, and on the basis of them, engineers constitute a ventilation project, focusing on the norms specified in state documents. Below, we will give an example of this calculation of ventilation for a residential building, using the most simple ways: in multiples, sanitary standards and total area.
Calculation of multiplications
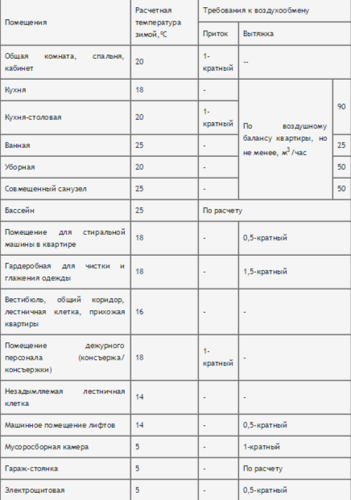
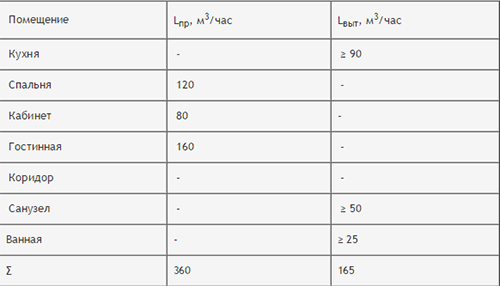
This calculation is quite complex, but still feasible. The table below shows the ventilation regulations necessary for the work of calculations.
Before it is worth explaining what kind of multiplicity is. This is a magnitude showing how many times for 1 hour the air in the house was replaced by fresh. Multiplicity depends on the specifics of the building and its area. For example, consider a single air exchange - this means that in an hour from the room was derived and at the same time came the amount of air equal to the volume of this building itself. In the 2nd Table Speakers, you will find the requirements for ventiling on the influx and exhaust air.
The calculation is made according to the formula: L \u003d n * V (cubic meters / hour), where n is a multiplicity (view in the table), and V is the volume of the room.
To calculate the ventilation for the whole house consisting of several rooms, consider from "without walls", that is, as one room with a common air volume. To do this, find out the volume of each room multiplying the length, height and width of the walls, and then use the above formula.
It is worth noting that for most rooms it is possible to do only a tributary or hood, but for spaces with high humidity (kitchen, bathroom) will need to organize a recycling system. If the table is stuck, then the room does not need ventilating. As a result, you should have the equation of the volume of inflow and exhaust volume. If this did not happen, the number of air exchange in these rooms can be increased to the required indicator.
If a table is not specified in the table, calculate the rate of ventilation rate of residential premises according to 3 cube air per hour per hour. m, that is, according to the formula: L \u003d S * 3, where S is an area of \u200b\u200bthe room.
All values \u200b\u200bl must be multiple of the number 5, so if necessary, round them up to five to the biggest side. Calculate L for all rooms individually first for air inflows, then - for drawing, fold the indicators and compare the total l of influx and l hoods - they must be equal. If the value of the tributaries turned out more exhaust, then to keep the balance to increase the air exchange for those rooms where the air exchange was minimally permissible.
Calculate ventilation by multiple houses with a quadrature of 140 kV. m with such rooms:
- the kitchen is 20 square meters. m (S1);
- bedroom for 24 square meters. m (S2);
- the working office is 16 square meters. m (S3);
- the living room is 40 square meters. m (S4);
- hall - 8 square meters. m (S5);
- toilet - 2 square meters. m (S6);
- bathroom - 4 square meters. M (S7).
The height of the ceilings at the same time is 3.5 m. A young couple lives in the house without children.
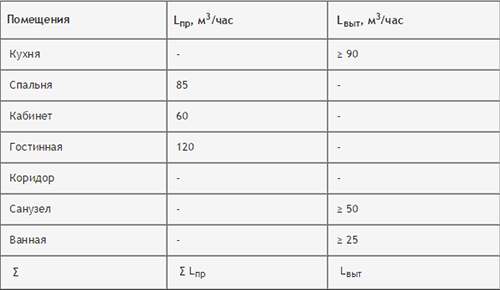
It is necessary to calculate the volume of rooms, multiplying the square to the height of the ceilings. As a result, we get the kitchen \u003d 70 cubic meters, bedroom \u003d 84, Cabinet \u003d 56, living room \u003d 140, hallway \u003d 28, toilet \u003d 7 and bathroom \u003d 14 cubic meters.
Next, calculate the required amount of air according to the formula L \u003d n * v, write data into the table and round the values \u200b\u200bup to 5.
There is no multiplicity for the living room in the first table, so it can be calculated for it, based on the fact that 1 square meter. The room of the room requires 3 cubic meters of air per hour. We multiply the area of \u200b\u200bthe living room at 3 and we get 120 cubic meters per hour.
Now it remains to fold the air exchanges of all rooms for the influx and separately for the exhaust and compare these indicators. It turned out that the influx was 265 cubic meters, and the extract was 165, so it must be increased. Add drawing values \u200b\u200bfor those rooms where stronger ventilation is required or where the values \u200b\u200bwere minimally allowed - in the bathroom and kitchen.
In the toilet and the bathroom it is better to install only an exhaust, and in the bedroom, living room and desktop - only the influx. This measure will prevent the stacking of unpleasant odors.
Sanitary standards
To calculate air exchange in an administrative and public or public building on sanitary standards, you will need to know an approximate number of people constantly located. According to the norms of a person who is constantly located in the room, at least 60 cubic meters of fresh air must be needed, 20 cubic meters will be enough to a temporary visitor.
Calculate the air exchange for the same house. If you recall the norms per person, it will turn out to be a formula (for a bedroom): L \u003d 2 (Human) * 60 cubic meters. To calculate the air exchange for the office, one constant and one temporary person should be taken into account: l \u003d 1 * 60 + 1 * 20. In the living room, the young couple is sometimes found with two-three friends or parents, so there should also be considered temporary visitors for this room.
If you calculate the air exchange for all rooms, taking the data from the first table, it will become obvious that the volume of fresh air is much larger than the exhaust volume, and therefore the drawing data should be increased by adding 195 cubic meters / hour to create a balance. It is recommended to increase evenly, distributing in all rooms, but you can apply in one room that needs ventilating, such as in the kitchen or bathroom. That is, the volume of volume in the kitchen should be added 195, and it will be 285 cubic meters per hour.
The spent air from the other large rooms will move into the kitchen and go out through the hole through natural thrust or sucking with exhaust fans. It is very important to ensure such a movement of the air masses so that smells and moisture in the apartment are stood.
Calculation by Square
To calculate ventilation in the area, it is necessary to consider that for residential buildings, the Regulation implies the submission of 3 cubes of fresh air per hour to an area of \u200b\u200b1 square. m. It does not matter how many people are inside.
It remains to calculate the ventilation in the area, and for this we propose to solve the simple equation: l of influx \u003d l exhaust \u003d s all at home * 3.
Production calculations, we have the following picture: L exhaust 3 \u003d 114 * 3 \u003d 342 cubic meters / h
Summarizing
Of all the above examples, it can be seen that the meaning of the air exchange in each of the options is different, but they are all considered correct. What of them are guided by - to solve you, but the calculation on the area and multiples will cost more cheaper than by sanitary standards. It also guarantees more comfortable conditions for life, so often the decisive factor in choosing the ventilation system is the financial position of the customer.
Selection of an air duct
When the calculations are completed, you can proceed to the choice of the ventilation scheme of the premises, that is, think over the plan, make drawings and choose equipment. Today, rectangular and round air ducts are used for ventilation systems. If you choose a rectangular air duct, watch the side aspect ratio to exceed 3: 1, otherwise the ventilation will be constantly noise, and the pressure in it will not be high enough (there will be no traction).
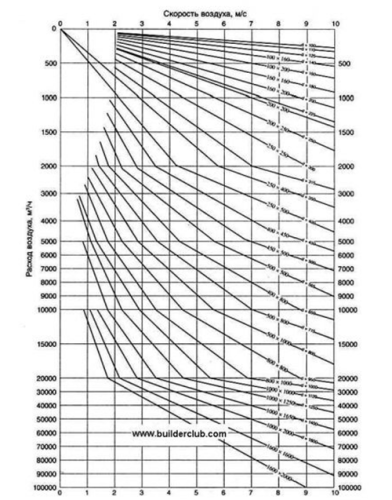
Also, when choosing, it is necessary to take into account that the normal speed in the highway should reach about 5 m / s (in branches of approximately 3 m / s). To determine the required section sizes, use the diagram below - it shows the dependence of the size of the section from the flow of air and the speed of its movement. The horizontals marked air flow, verticals - speed, oblique lines - the corresponding duct dimensions.
Select the desired cross section of the highway, which will go to each room and the most highway highway so that the air is supplied to the cost of 360 cubic meters per hour (as in the example with our home).
If you organize a natural exhaust, the air flow rate in the highway according to the norms should be no more than 1 m / h. The calculation of exhaust ventilation of the room should occur taking into account the normalized air velocity no more than 5 m / s for a highway and 3 m / s - for branches.
We hope this article will help you correctly calculate air ventilation indoors and make your home comfortable. Competently produced calculations allow you to save not only on the arrangement of the ventilation system, but also on overhaul in the distant future.