Which insulation is better to use under siding Useful advice,Walls,Construction,Building materials

Is additional thermal insulation need for home? To find the answer to this question, it is necessary to analyze, three items: from which material the building is built, whether additional facade cladding will be, and which climate in the area where the house was built.
Content
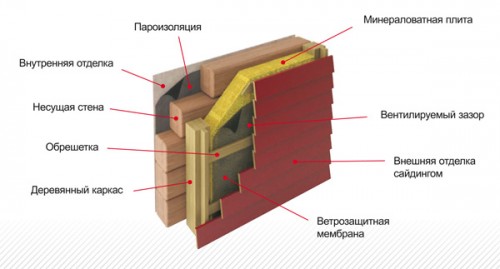
First of all, an additional insulation for walls is required by those houses that will be used for year-round accommodation. For summer houses, insulation does not need to do. In addition, if you definitely decided to build a house by siding, then without additional thermal insulation you can not do, as the air layer between siding and the wall will not be able to preserve and increase heat. On the contrary, it is fraught with the destruction of the walls, as moisture will certainly accumulate here. And the thermal insulation will serve as a kind of thermos - it will be able to not only give heat into the stub, but also a pleasant coolness during the exhausting heat. But approach the choice of insulation for the walls under siding must be responsible, because there are many different materials on the market, which have both their advantages and their cons.
Requirements for insulation
Experts claim to ensure that the insulation fulfill his duty and fulfill all the functions assigned to it and, which is important, did not disappoint you, it must necessarily meet some requirements.
- The insulation material must have a low thermal conductivity coefficient. For example, modern heaters have such a value within 0.030-0.042 - no more than.
- The insulation under the siding necessarily should not be sensitive to temperature drops.
- The material for the insulation must have low hygroscopicity.
- The insulation must be resistant to aggressive environmental impacts (whether it is either chemical components or organic).
- The insulation is precious to neutrally react to a sour or alkaline environment.
- The material for the insulation must be fireproof.
- The insulation under siding should have environmental qualities. True, it is necessary to give a report that this factor can serve as a favorable component for the development of various forms of life: fungi, bacteria, mold, insects, small rodents, etc.
- The insulation must be so dense not to lose its shape.
Which thickness must be laid insulation
The best insulation for siding is the necessary level of thermal insulation. But, before you go for the purchase, you need to find out, the building material of the walls - because it depends on the layer of the insulation, which you need.
- Walls - concrete, thickness from 230 mm and more - insulation thickness from 150 mm and more.
- Walls - brick (silicate, empty, red burned), thickness 510 mm - a heater with a thickness of 100 mm.
- Wall - timber (coniferous wood), thickness 150 mm - insulation 100 mm.
- Walls - Bar, thickness 200 mm - 50 mm insulation.
Do not forget that good thermal insulation is also windproof, which will perfectly cope with waterproofing. But you should not use a waterproof film, as it will only contribute to the flue of the insulation, and this will reduce its insulating quality. That is, choosing the material, remember that it should be diffuse: to protect from wind and moisture outside, and from the inside - not to give a steam out.
What insulation under siding select?
In fact, the selection of insulation under siding is not so big - mostly, it all depends on the price and method of laying (speed, simplicity, etc.). The most common kinds of insulation are the following building materials.
Mineral wool
- Mineral wool is a fibrous material that is made of waste metallurgy, silicates, basalts and various other rocks.
- The price of this material is varied - it all depends on the difference in indicators.
- Mineral wool can be insulated any walls: from wood, blocks, bricks.
- This insulation has a very low thermal conductivity.
- Minvat is perfectly combined with both plastic and metal siding, but for this it is necessary to acquire semi-rigid wool in the form of plates. Its dimensions 1m x 0.5m. The thing is that the rolled cotton will be more difficult to attach to the walls, and she can slip down. Unlike stoves - they are most comfortable, and they keep much better.
- Mineral wool is a non-combustible material.
- Minvat does not create a lot of dust, it must be wrapped with a vapor barrier film - it will also become an obstacle to a water vapor that penetrates the walls into the ventilation gap.
- Mineral wool fibers perfectly absorb various noises.
- Mineral wool preserves warmly.
- Large disadvantage of minvati is its high water absorption coefficient - almost up to 70%.
Ekwata.
- This material in terms of environmentally friendly is the highest rating.
- Equata, despite the fact that there is cellulose in its composition, does not burn and does not rot.
- Eco-out is hard to mount on the wall, as it is not yet released in the form of hard panels.
- For fastening, eco-plants need special equipment - it is with its help that this material can be applied to use as a heater. Thanks to the special equipment, the EcoWat will be firmly held on the wall, not slipping and will not give a shrinkage.
- Equata perfectly absorbs various noise due to its loose structure.
- Equouth saves warmth.
Glass Vata.
- Glasswater is a type of mineral wool, it is made of glass industries.
- Glasswater has a great thermal conductivity.
- Glass wool perfectly absorbs water.
- This material is not lit.
- Glasswater has a greater density - up to 30 kg per m3.
Styrofoam
- This polymer material has both low water absorption and low thermal conductivity.
- This insulation is produced in the form of plates of various density and thickness - from here and different prices. It contains a variety of vibrant bubbles that are filled with gas.
- The foam flaggy is very high: 1 - 4.
- Polyfoam is comfortable and easy to install, as it is hard, but lightweight, which allows you to fine with the walls. Fasten the best plate dowels.
- Currently, the price of this insulation is about the same with the Minvata, therefore, choosing a foam, it does not mean to "save".
- The material is short-lived - the maximum foam can serve 15 years, no more, since polymers are very quickly destroyed.
- Polyfoam has very low vapor permeability, so there is no natural air exchange in the house, and the building turns into a peculiar thermos.
- To get rid of excess moisture in a house, insulated foam, you often need to ventilate the premises, or use mechanical ventilation. It is fraught with heat loss in the rooms.
- Polyfoam does not absorb, but on the contrary, enhances the sound.
- Polyfoam is best insulated with various engineering communications (for example, water supply or sewage), or concrete ties of the floor - there will be ideal thermal conductivity and a minimum of moisture absorption.
Extruded polystyrene foam (EPPS)
- This material has low thermal conductivity.
- Extruded expanded polystyrene has a high degree of water absorption.
- EPPS has a very high density - up to 40 kg per m3.
- Extruded polystyrene foam is made from a conventional polyterol, from which aircases are squeezed under high pressure.
- Extruded polystyrene foam is a very flammable material - it has 1-4 degree.
And, finally
- Choosing a heater, remember that this work will also have to pay money. At the same time, the most expensive "pleasure" will be applied for Eco.
- When comparing the value indicators of all the above insulation, the lowest price has an eco-room. A little more expensive will cost plates from polystyrene and mineral wool.